用 Wireshark 分析 TCP Segmentation Offload (TSO)#
Analyzing TCP Segmentation Offload (TSO) with Wireshark#
Most modern PCs and servers have powerful network interface chip sets that can provides TCP/IP functionality that cuts the load on the host machine. The most common of these functions is TCP Segmentation Offload (TSO). In this short article we use Wireshark to discover how TSO affects our interpretation of network traces.
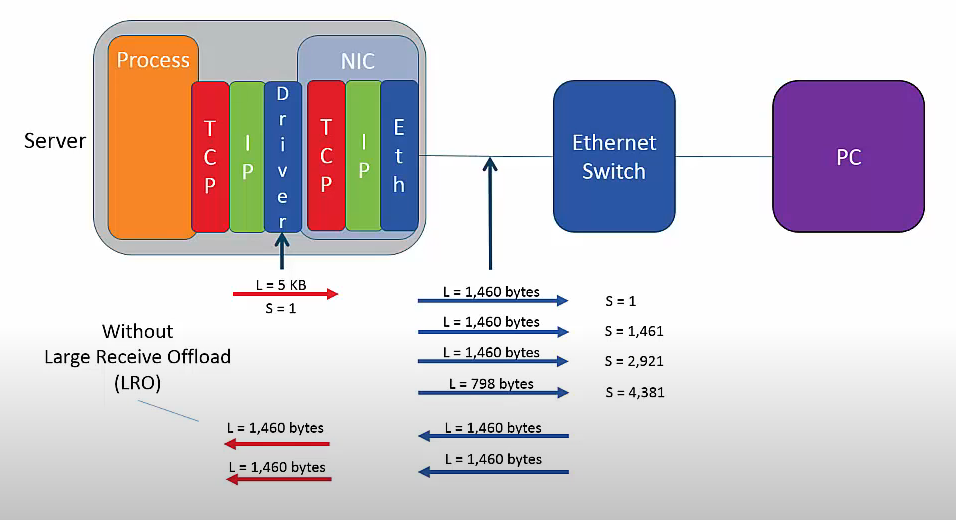
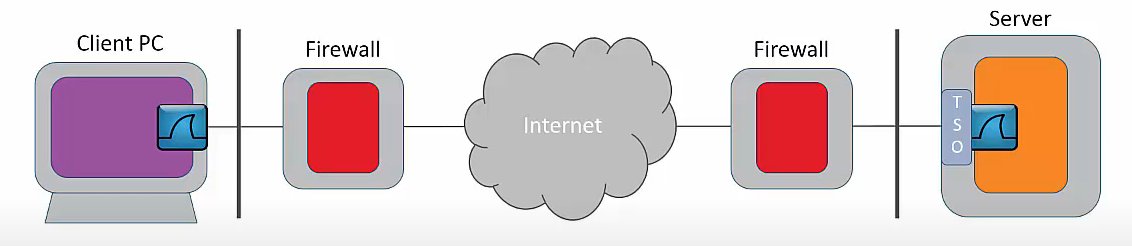
A program running in a PC or server may make a single call to the TCP/IP stack to send, say, 5 KB of data. The TCP/IP stack, which is a software driver within the operating system, must repackage the 5 KB so that it can be sent in multiple packets. This operation is called segmentation and it consumes CPU cycles. Additionally, the TCP/IP stack must handle issues such as retransmissions.
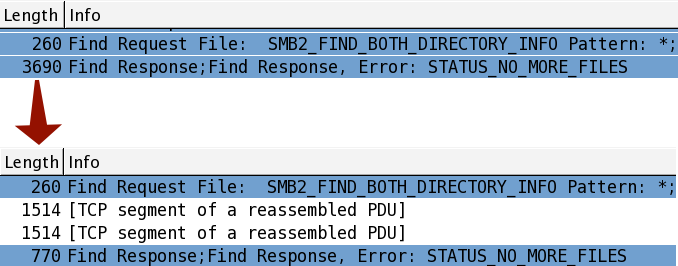
A network interface chip set that provides TSO allows the host TCP/IP stack to send a single 5 KB segment. The network interface chip set then re-segments the data into, say, three packets with a TCP Length of 1,460 bytes and one of 798 bytes, making 5 KB in total. This can all appear to be very confusing in a network trace, especially as the packets received may not be aggregated in a similar manner.
How Can the Packet Size Be Greater than the MTU?#
TCP Segmentation Offload (TSO) 的配置#
# display
$ ethtool -k eth0 | grep offload
tcp-segmentation-offload: on
udp-fragmentation-offload: off
generic-segmentation-offload: on
generic-receive-offload: off
large-receive-offload: off
# set
$ ethtool -K eth0 tso off
